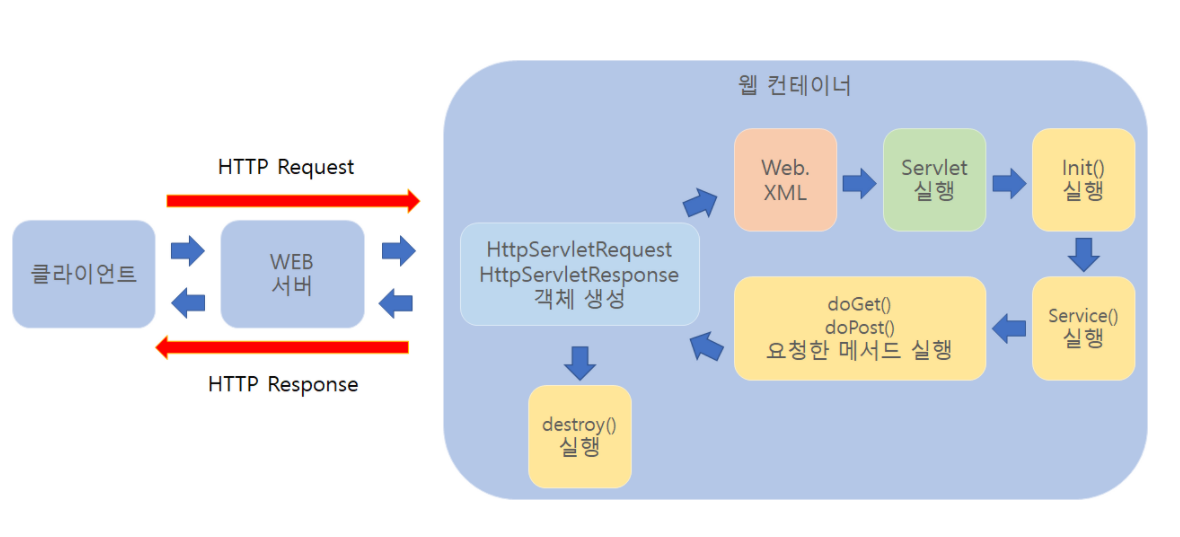
서론
휴대폰과 이메일 중 압도적으로 휴대폰 사용량이 높다고 생각했고
이메일은 가입 시 인증받지 않는 곳도 많기 때문에 우선적으로 휴대폰인증을 구현하려고 했다.
이메일은 필요 시 SMTP 활용하여 구현 예정
기능 구현을 위해 찾아본 아래의 API 중 coolsms를 선택했다.
1. 네이버 SMS
2. Twilio
3. coolSMS
네이버는 한달에 50건이 무료고, Twilio는 가입 시 15달러를 준다고 한다.
cool sms 사용하기
들어가기 앞서 유료임.. SMS를 보내는 것이기 때문에 당연한가 ?
세상에서 가장 안정적이고 빠른 메시지 발송 플랫폼 - 쿨에스엠에스
손쉬운 결제 전용계좌, 신용카드, 계좌이체 등 국내 결제 뿐만 아니라 해용신용카드로 한번의 카드번호 등록으로 자동충전까지 지원합니다. 전용계좌, 신용카드, 계좌이체 등 다양한 결제 방식
coolsms.co.kr
사이트에서 회원가입 및 API KEY, SECRET KEY를 발급받았고
COOLSMS
세상에서 가장 쉽게 메시지를 발송할 수 있도록 도와드립니다. COOLSMS has 20 repositories available. Follow their code on GitHub.
github.com
공식 github가 있고, API 사용 시 예제까지 잘 있으니 참고해서 작성하도록 하자.
적용하기
1. 공식문서 샘플 코드
implementation 'net.nurigo:sdk:4.3.0'//공식 서
public class ExampleController {
final DefaultMessageService messageService;
public ExampleController() {
// 반드시 계정 내 등록된 유효한 API 키, API Secret Key를 입력해주셔야 합니다!
this.messageService = NurigoApp.INSTANCE.initialize("INSERT_API_KEY", "INSERT_API_SECRET_KEY", "https://api.coolsms.co.kr");
}
}//공식 문서
public ExampleController{
@PostMapping("/send-one")
public SingleMessageSentResponse sendOne() {
Message message = new Message();
// 발신번호 및 수신번호는 반드시 01012345678 형태로 입력되어야 합니다.
message.setFrom("발신번호 입력");
message.setTo("수신번호 입력");
message.setText("한글 45자, 영자 90자 이하 입력되면 자동으로 SMS타입의 메시지가 추가됩니다.");
SingleMessageSentResponse response = this.messageService.sendOne(new SingleMessageSendingRequest(message));
System.out.println(response);
return response;
}
}
2. 내 서비스에 맞게 바꾼 코드
DefaultMessageService 및 내 서비스에서 사용하는 UserService, 휴대폰 인증 로직을 수행해 줄 인증담당 Service를 의존성주입 해주었다.
인증담당 Service는 현재 PhoneValidation이지만 차후 이메일인증까지 수행할 경우 네이밍을 변경하여 같이 사용할 예정이다.
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/users")
public class UserController {
final UserService userService;
final DefaultMessageService defaultMessageService;
final PhoneValidationService phoneValidationService;
@Autowired
public UserController(UserService userService, PhoneValidationService phoneValidationService) {
this.userService = userService;
this.defaultMessageService = NurigoApp.INSTANCE.initialize("NCS1QZEXH48DE8O1", "12MPLZHBL3SP13B2EEDVNRRTW0Z6OO7O", "https://api.coolsms.co.kr");
this.phoneValidationService = phoneValidationService;
}
}
1. 인증 문자 보내기
@PostMapping("/validation/phone")
@ResponseBody
public SingleMessageSentResponse sendSMS(String phone, HttpSession ss) {
String ran_str = phoneValidationService.getValidationCode();
Message msg = phoneValidationService.getMsgForm(ran_str, phone);
SingleMessageSentResponse response = this.defaultMessageService.sendOne(new SingleMessageSendingRequest(msg));
ss.setAttribute("validation", ran_str);
ss.setAttribute("message_id", response.getMessageId());
ss.setMaxInactiveInterval(180);
return response;
}@Override
public String getValidationCode() {
String ran_str = "";
for(int i=0; i<6; i++) {
ran_str += (int)(Math.random()*10);
}
return ran_str;
}
@Override
public Message getMsgForm(String ran_str, String phone) {
Message msg = new Message();
msg.setFrom("01024402059");
msg.setTo(phone);
msg.setText("[randomchatUNI] 아래의 인증번호를 입력해주세요\n" + ran_str);
return msg;
}
1. 인증번호를 생성했다. 6자리의 랜덤한 숫자가 생성된다.
2. API에서 제공하는 Message객체를 리턴시켜 phone 에 들어있는 휴대폰번호로 인증메세지가 간다.
3. 세션에 임시로 SingleMessageSentResponse의 객체(API 제공) 중 인증에 활용할 수 있는 messageID의 Value를 유효기간을 담아 인증번호를 검증할 수 있도록 하였다.
3번의 경우. DB에 임시로 테이블을 생성해서, 유효기간이 만료되면 해당 Row를 삭제하게 할 지 세션에 등록할 지 고민하다가 세션으로 했다.
테이블과 세션 중 고려할 때
테이블은 insert, select, delete 쿼리를 한 인증에서 한 번이상 무조건 수행해야 하며, 인증시간이 만료됐을 때 delete를 또한 실행해야 하기 때문에 비효율적이라고 판단했다.
하지만 세션의 경우에도, 유효기간을 설정할 수 있지만, 세션을 이용한 다른 비즈니스 로직에도 영향을 끼칠 수 있다고 생각했다. 물론 여러 Session을 생성하여 관리하거나, 해당 세션의 Key값을 확실하게 기억할 수 있다면 예방할 수 있다고 판단했다.
근데 근본적으로, 해당 토이 프로젝트 내에서 세션을 활용하여 진행할 사항이 로그인, 로그아웃 시 세션을 등록하고 지우고 하는 것 밖에 없는데, 딱히 세션유효기간을 설정해서 사용하지 않을 것이기 때문에 Security만을 사용한 로그인 로그아웃을 사용하고 있기 때문에, 그냥 세션을 활용하기로 했다.
@GetMapping
public String signup(@AuthenticationPrincipal User user, HttpSession ss) {
if(user != null) return "redirect:/uni/main";
ss.invalidate(); //validation phone clear
return "users/signup";
}
또한 회원가입 페이지에 다시 접근 시, 세션을 초기화해주었다. 세션을 인증 이외에는 사용하지 않을 것이기 때문에 상관 없을 것다.
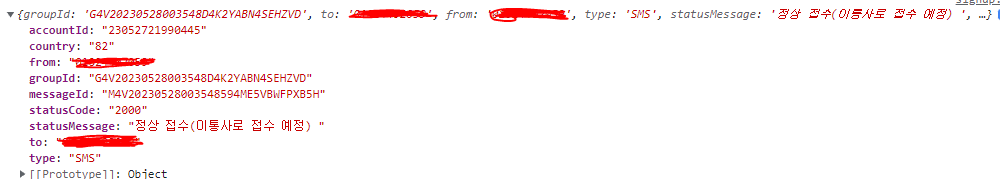
아래는 리턴받은 API의 response 객체이다.
2. 받은 인증번호 검증하기
@GetMapping("/validation/phone")
@ResponseBody
public String validationSMS(String validation, HttpSession ss) {
return phoneValidationService.validationSMS(validation, ss);
}@Override
public String validationSMS(String validation, HttpSession ss) {
if(ss.getAttribute("message_id") == null || ss.getAttribute("validation") == null) return "인증번호 만료, 처음부터 다시 시도해주세요";
else {
if(ss.getAttribute("validation").equals(validation)) return "인증 완료";
else return "인증 실패";
}
}
세션에 값이 없는 경우는 내가 설계한 로직에 어긋나는 것이고
인증번호 자체가 다른경우는 뭐.. 말할 것도 없다
3. 확인하기
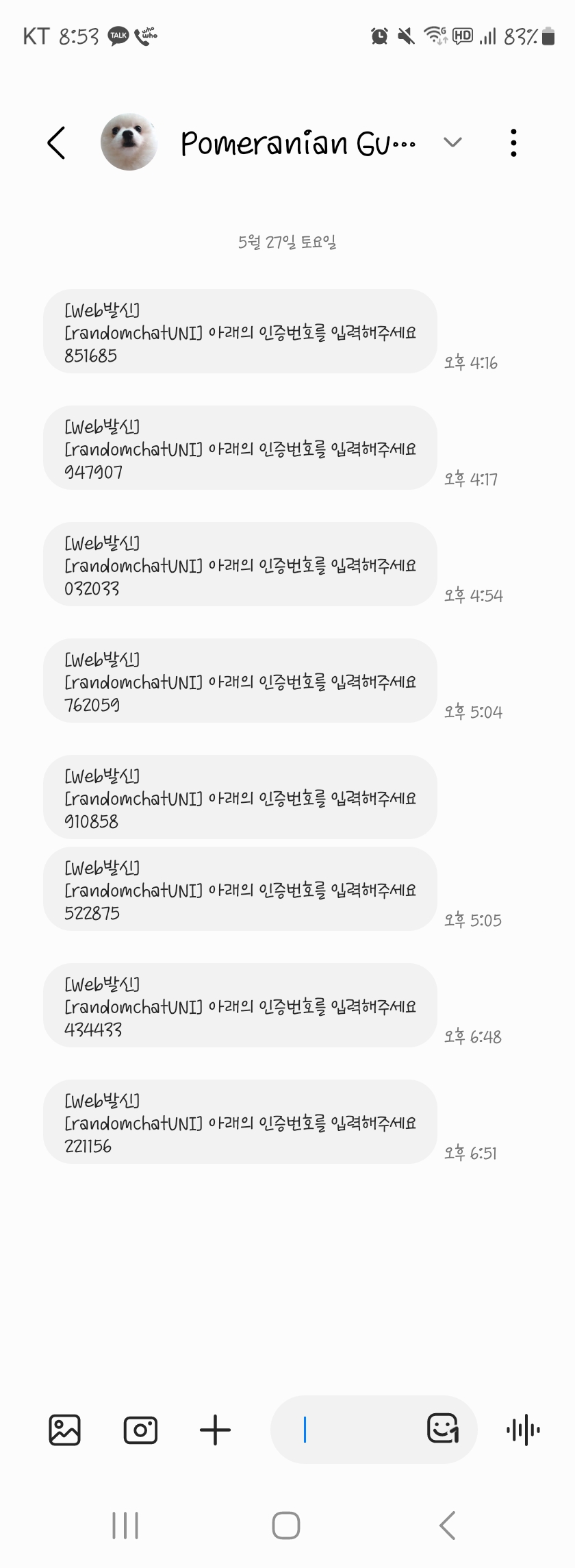
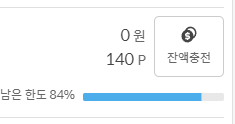
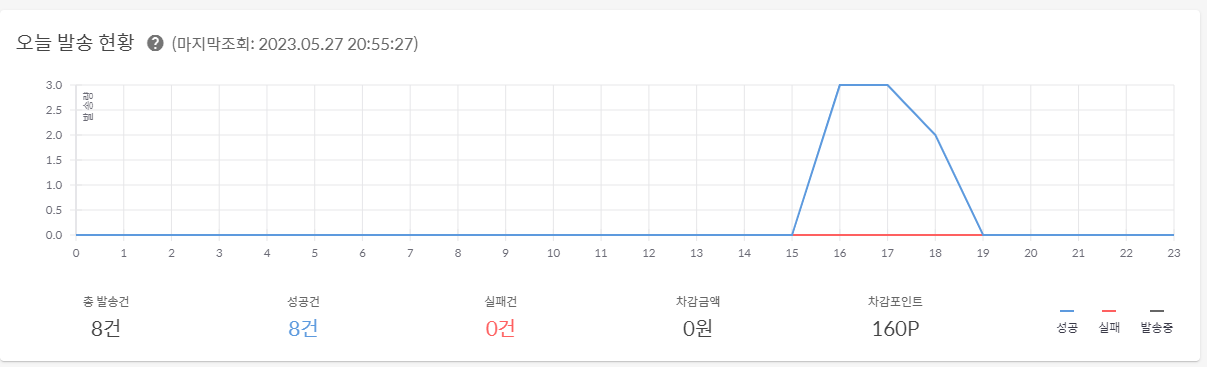
이래저래 검증해본다고 8통을 보냈는데
아무래도 coolSMS에서는 300원을 기본으로 주고 한통당 20원으로 책정하나보다